1. Core Disease Vaccination Program (Combined with Policies and Breeding Scenarios)
Mandatory Vaccines
- African Swine Fever (ASF): No commercial vaccine is available currently, relying on biosecurity measures (Key points: closed management, disinfection of vehicles/personnel, ban on feeding food waste).
- Classical Swine Fever (CSF): Piglets receive the first vaccination at 21 days old and the second at 60 days old; sows are vaccinated twice a year (6 months apart).
- Pseudorabies (PR): Piglets receive intranasal vaccination at 3 days old and a booster at 30 days old; sows are vaccinated twice a year.
- Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD): Piglets receive the first vaccination at 45 days old and the second at 75 days old; adult pigs are vaccinated once every 3 months (select vaccine subtypes based on locally prevalent strains).
Optional Vaccines:
Vaccines for Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), Porcine Circovirus Disease (PCVD), Transmissible Gastroenteritis (TGE), Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea (PED), etc., can be administered according to local disease prevalence (PRRS vaccines require cautious selection to avoid strain conflicts).
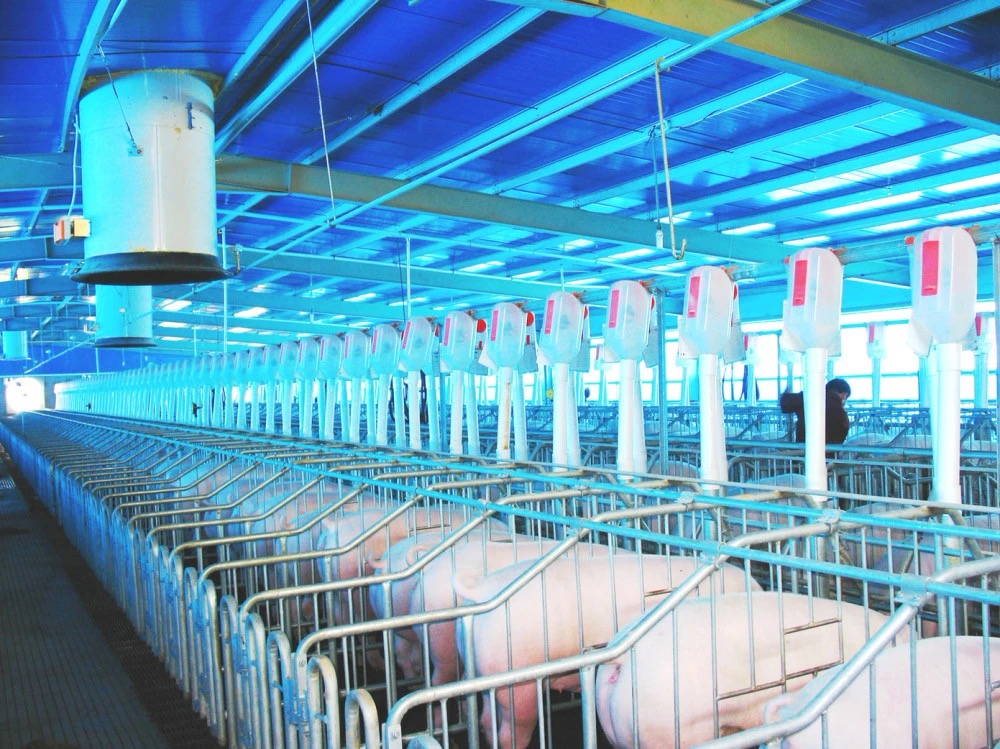
2. Biosecurity Measures (Top Priority, Especially for ASF Prevention)
Pig Farm Zoning:
Divide the farm into living areas, production areas, isolation areas, and manure treatment areas, with disinfection channels between each zone.
Personnel Management:
- Personnel entering the farm must take a shower, change clothes, and undergo disinfection.
- Visiting other pig farms is prohibited; external personnel are not allowed to enter the production area.
Vehicle Disinfection:
- Separate vehicles for transporting pigs, feed, and manure must be used.
- Before entering the farm, vehicles undergo high-pressure washing + disinfection with agents (e.g., peracetic acid, sodium hydroxide) and are left to stand for at least 30 minutes.
Material Management:
- Feed, veterinary drugs, and other materials must be disinfected upon entry; carrying pork and pork products into the farm is prohibited.
Rodent and Vector Control:
- Regularly place rodenticides (to prevent accidental ingestion by pigs).
- Clear weeds and stagnant water around the farm to reduce disease transmission vectors.
3. Standardized Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
- Immediately isolate sick pigs to avoid cross-infection; diagnosis must be conducted by professional veterinarians (self-diagnosis and arbitrary medication are prohibited).
- Strictly comply with veterinary drug usage regulations:
- Use formal veterinary drugs with approved registration numbers.
- Administer drugs according to specified dosages and treatment courses; avoid antibiotic abuse (e.g., florfenicol and cephalosporins require a withdrawal period).
- Withdrawal Period Management:
- Finishing pigs must meet the specified withdrawal period before slaughter (e.g., 7-14 days for antibiotics).
- Early slaughter is prohibited to prevent drug residues.
- Suspected ASF Cases:
Post time: Nov-26-2025